About Dioxins
What are Dioxins?
The term"Dioxins" are defined to include PCDDs, PCDFs, Co-planar PCBs by the Law Concerning Special Measures against Dioxins.The general structures of dioxins molecule are shown on the Fig.1. The numbered positions in this figure are attached by chlorine.
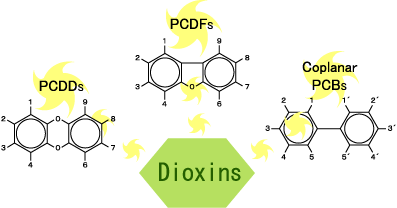
Fig.1
Kinds and Toxicity of Dioxins
There are 75 kinds of PCDDs, 135 kinds of PCDFs and more than 10 kinds of PCDFs by the difference of attached position by chlorine. And 29 kinds of Dioxins have toxicity. Toxicity of dioxins varies from compound to compound. 2,3,7,8- TCDD (Fig.2) is known to possess the highest toxicity.
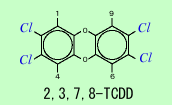
Fig.2
Characteristic of Dioxins
Dioxins are generally quite stable. They in general are colorless solids with properties of high fats and oils solubility . They do not reacting easily to other chemical substances and acids, but are tough to gradually decompose with exposure of ultraviolet light.
Units
Even if the amounts of dioxins are extremely small, their toxicity is so strong that we have to consider the influence on people and environment. "ppt" is one of the measurement units, and "ppt" is useful to indicate the micro level of concentration. "ppt" means 10 to the minus 12.
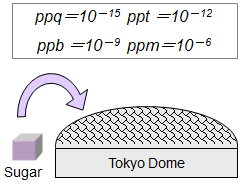
If water were held in a container of the size of Tokyo Dome and a cube of sugar were dissolved in the water, the result would be 1 ppt level
The acute toxicity of dioxins
This figure shows the acute toxicity comparison between dioxins, sarin, cyanide and DDT. It is said that dioxins are "the most toxic of the man-maid chemicals".
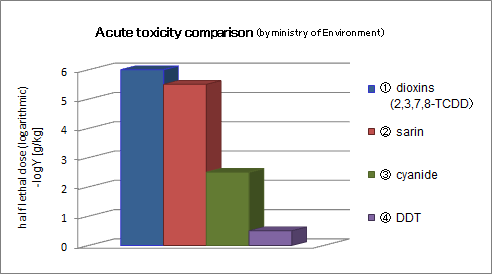
Emissions of dioxins
It is assumed that about 90% of the dioxins emissions comes from the incineration of household and industrial waste in Japan.

Impact of dioxins on the environment
The average dioxin concentrations in the environment in Japan revealed in a 1999 survey are about 0.18pg/m3 for the ambient air and about 6.5pg/g for the soil and about 0.24pg/l for the water .Summary
We should realize that a serious issue that we are facing is not acute toxicity of high doses of dioxins but chronic toxicity of extremely small doses of dioxins. Then we should do research on how much dioxin we take in every day life and what the risks of dioxins to humans are. For those purposes, researches are taking place about how dioxins are formed,environmental assessment of dioxins, analyzing technique, concentration of dioxins in foods and breast milk. Dioxins are not produced intentionally. Since dioxins are emitted by incineration, reducing the amount of waste is an effective way to lessen dioxin release. So we should clearly recognize the importance and emergency of dioxins issue one by one, and try to reduce dioxins emission. Not only leadership of government, but also personal efforts can contribute to the serious issue.
literature cited:Ministerial Council on Dioxins Policy「Dioxins 2001」
Contact us
- MLAP Team, Accreditation Division for Metrology, International Accreditation Japan (IAJapan), National Institute of Technology and Evaluation
-
Phone number:+81-3-3481-1633
Fax number:+81-3-3481-1937
Address:2-49-10 Nishihara, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 1510066, Japan MAP
Contact Form


