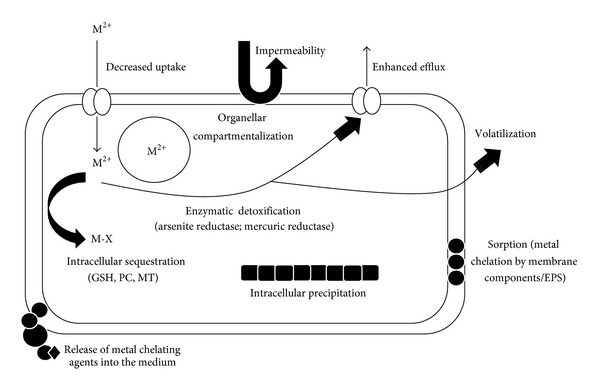
General mechanisms adapted by bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea for metal resistance. --Srivastava (2013). Figure 1

金属耐性
概要
金属耐性とは通常では生育が阻害される金属の存在下においても生育可能とする生物の機能。
金属が毒性を示すメカニズムは3つ。
これらに対抗する機能を有する細菌を金属耐性細菌と呼んでいる。
- 酵素、transport systemのブロック
- 必須イオンのdisplacement and/or substitution
- 生体分子の活性型高次構造 (active conformation) を修飾
機能に関する知見
機能を示すメカニズム
金属耐性のメカニズムは5つに分けられる。
- 細胞内への侵入をブロック (permeability barrier)
-
細胞外への排出 (active efflux)
ヒ素耐性 (NFUNC_0004)
-
細胞内で隔離 (by metal-binding protein)
メタロチオネイン (NFUNC_0006)
- 細胞外で隔離 (by extracellular polysaccharides)
- 酵素による金属の無毒化 (enzymatic detoxification)

参考文献
- Dopson, M. et al. (2003). Growth in sulfidic mineral environments: metal resistance mechanisms in acidophilic micro-organisms. Microbiology. 149(8):1959-1970. PMID: 12904536

- 國頭 恭, 松本 聰 (2010) 「土壌中の重金属耐性微生物の生態と浄化への利用」 『地球環境』 15(1), 37-44.
- Srivastava, P. and Kowshik, M. (2013). Mechanisms of metal resistance and homeostasis in haloarchaea. Archaea. 2013:732864. PMID: 23533331

MiFuPへのリンク
水銀耐性
- NFUNC_0005 Mercury resistance
NRULE_0008 Mercuric reductase
ヒ素耐性
- NFUNC_0004 Arsenical resistance
NRULE_0014 Arsenical pump-driving ATPase
NRULE_0015 Arsenical pump membrane protein
NRULE_0016 Arsenite resistance protein ArsB
NRULE_0017 Arsenate reductase
NRULE_0018 Arsenate reductase
NRULE_0019 Arsenate reductase
NRULE_0020 Arsenical resistance operon trans-acting repressor ArsD
NRULE_0021 ArsH protein
メタロチオネイン
- NFUNC_0006 Metallothionein
NRULE_0009 Metallothionein
(更新日 2014/03/13)